OLA on Windows via VMWare
This explains how to run OLA on a Windows system using VMWare. This uses virtualization so it’s not recommended for real time lighting control. However it’s useful if you want to experiment with OLA and perform tasks that aren’t time sensitive like the RDM Responder Tests
Contents
Prerequisites
- A Windows PC with a working internet connection.
- At least 20G of free hard disk space. Chance are you won’t need that much.
Setting up the Linux System
This tutorial is based on these excellent instructions. The instructions are for Windows 7, but works fine on XP as well.
Download & Install VMWare Player
Download the free VMWare Player. You’ll need to complete the survey and provide an email address. Install this on your windows machine. Reboot.
Download & Install Linux Distribution
I recommend Ubuntu. It’s fairly easy to use and stays up to date. Get the latest version from here. Once this is done you should have an .iso file which will be around 600MB.
Setup a New Virtual Machine
Open VMWare Player, select “Create New Virtual Machine”. Choose “Installer Disk Image” and point to the Linux .iso file you downloaded.
On the next screen setup a username & password. You can then control where the VM image is stored and the size of the image. The defaults are fine.
Click Finish to setup the Linux image. Installation of Ubuntu then begins.
You’ll be asked if you want to install VMWare tool for Linux. Say yes as we’ll use them later. The download will continue along with the install. This stage can take quite a while.
Once complete, you’ll be presented with a graphical login screen showing the username that you setup before. Login to the system and you’ll be shown the desktop.
Next enter Unity mode. This seamlessly merges the Linux windows with the Windows desktop. You can also copy and paste between Windows and Linux at this point.
Finally open the Linux terminal application as shown below. You’ll need to move your mouse to the Start button for the Unity menu to appear.
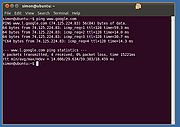
Now we’ll confirm that the network is working. Type:
ping www.google.com
You should see responses like what’s below. Hit Control-C to exit the ping program.
At this point we have a working Linux system. Time to install OLA
Installing OLA
These instructions closely follow OLA on Linux.
Install the dependencies
sudo apt-get install libcppunit-dev libcppunit-1.13-0 uuid-dev pkg-config libncurses5-dev libtool autoconf automake g++ libmicrohttpd-dev libmicrohttpd10 protobuf-compiler libprotobuf-lite10 python-protobuf libprotobuf-dev libprotoc-dev zlib1g-dev bison flex make libftdi-dev libftdi1 libusb-1.0-0-dev liblo-dev libavahi-client-dev python-numpy
Note: Some distributions may offer older versions of packages. For example, libprotobuf-lite6 or libprotobuf-lite7 instead of libprotobuf-lite8.
If you’re using Ubuntu 12.04 or later you can just use the command above. In earlier versions of Ubuntu the version of libprotobuf is too old, so you’ll need to install them by hand. You may also need to install an older version of libmicrohttpd (libmicrohttpd9 rather than libmicrohttpd10).
Then run ldconfig:
sudo ldconfig
Checkout or Download an Archive
You can either download a tarball, or pull the latest version from the git repo
Tarball
Download the most recent tarball from Github.
Extract using
tar -zxf ola-0.X.Y.tar.gz cd ola-0.X.Y
Git
If you don’t have git yet, you’ll need to install it with your distro’s package manager. On Debian / Ubuntu run:
sudo apt-get install git
Check out the git repo with the following command:
git clone https://github.com/OpenLightingProject/ola.git ola cd ola
Configure, build and test OLA
Type these
autoreconf -i ./configure --enable-rdm-tests make make check sudo make install sudo ldconfig
If you want to do RDM responder testing you must add –enable-rdm-tests
Using OLA
At this stage you can start OLA by running
olad -l 3
The -l flag controls the logging level from 0 (log nothing) to 4 (debug logs). 3 is log level info, which is usually enough for most people.
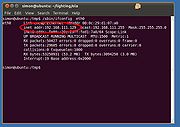
Now find the IP address of your Linux instance:
/sbin/ifconfig eth0
Look for a line that starts with inet addr:.
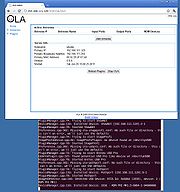
Open up a browser on the Windows PC and type in the IP address followed by :9090. This will bring up the OLA web console.
USB Devices
When using OLA with VMWare you need to make sure that any DMX USB devices are correctly bound to the guest OS (Linux).
http://www.vmware.com/support/ws45/doc/devices_usb_ws.html describes how to set this up.
Updating OLA
From time to time you may want to update the code. Assuming you checked out from git, from within the existing ola directory run:
git pull autoreconf -i ./configure --enable-python-libs make make check sudo make install
Not all of these steps are required each time, but unless you have a good idea of what changed it’s easier just to run everything.
See Also
- Building OLA for Windows – In the future this may provide a workable alternative